文艺平衡树
传送门:文艺平衡树
题意:给了一个长度为n n n m m m m m m
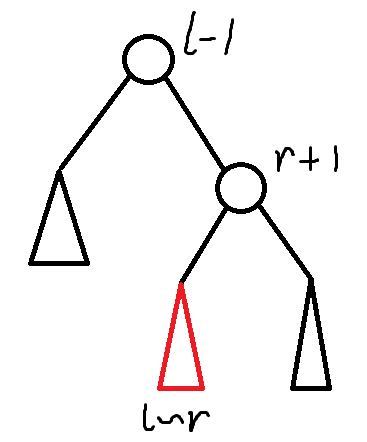
思路:平衡树的一道模板题,s p l a y splay s pl a y [ l , r ] [l, r] [ l , r ] l − 1 l - 1 l − 1 r + 1 r + 1 r + 1 l − 1 l - 1 l − 1 s p l a y splay s pl a y
红色的就是我们要翻转的区间,我们只需要在红色这个子树的根节点上打上翻转标记就行。
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;template <class T >struct Splay { struct Node { T val, lazy; int cnt, siz, fa, son[2 ]; }; vector<Node> tree; int root, idx; Splay () : root (0 ), idx (0 ), tree (1 ) {} Node& operator [](int x) { return tree[x]; } int ls (int u) return tree[u].son[0 ]; } int rs (int u) return tree[u].son[1 ]; } void pushup (int u) tree[u].siz = tree[ls (u)].siz + tree[rs (u)].siz + tree[u].cnt; } void pushdown (int u) if (!u || !tree[u].lazy) return ; if (ls (u)) tree[ls (u)].lazy ^= 1 ; if (rs (u)) tree[rs (u)].lazy ^= 1 ; swap (tree[u].son[0 ], tree[u].son[1 ]); tree[u].lazy = 0 ; } void rotate (int x) int y = tree[x].fa; int z = tree[y].fa; int k = (rs (y) == x); pushdown (x); pushdown (y); tree[z].son[rs (z) == y] = x; tree[x].fa = z; tree[y].son[k] = tree[x].son[k ^ 1 ]; tree[tree[x].son[k ^ 1 ]].fa = y; tree[x].son[k ^ 1 ] = y; tree[y].fa = x; pushup (y); pushup (x); } void splay (int x, int goal) while (tree[x].fa != goal) { int y = tree[x].fa; int z = tree[y].fa; if (z != goal) { ((ls (y) == x) ^ (ls (z) == y)) ? rotate (x) : rotate (y); } rotate (x); } if (!goal) { root = x; } } int findKth (int k) int u = root; while (true ) { pushdown (u); if (k <= tree[ls (u)].siz) { u = ls (u); } else if (k <= tree[ls (u)].siz + tree[u].cnt) { return u; } else { k -= tree[ls (u)].siz + tree[u].cnt; u = rs (u); } } return -1 ; } void insert (T val, int cnt = 1 ) int u = root, fa = 0 ; while (u) { pushdown (u); if (tree[u].val == val) { tree[u].cnt += cnt; tree[u].siz += cnt; splay (u, 0 ); return ; } fa = u; u = tree[u].son[val > tree[u].val]; } u = ++idx; tree.push_back (Node ()); if (fa) { tree[fa].son[val > tree[fa].val] = u; } tree[u].val = val; tree[u].fa = fa; tree[u].cnt = cnt; tree[u].siz = cnt; splay (u, 0 ); } }; int n, m;void print (Splay<int >& tree, int u) if (!u) return ; tree.pushdown (u); print (tree, tree.ls (u)); if (1 <= tree[u].val && tree[u].val <= n) { cout << tree[u].val << " " ; } print (tree, tree.rs (u)); } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (nullptr ); cin >> n >> m; Splay<int > tree; for (int i = 0 ; i <= n + 1 ; i++) { tree.insert (i); } while (m--) { int l, r; cin >> l >> r; int x = tree.findKth (l), y = tree.findKth (r + 2 ); tree.splay (x, 0 ); tree.splay (y, x); tree[tree.ls (y)].lazy ^= 1 ; } print (tree, tree.root); return 0 ; }
T-shirts
传送门:T-Shirts
题意:有n n n c i ci c i q i qi q i m m m i i i v i vi v i q i qi q i q i qi q i
思路:对于这种题,我们要么是维护T恤,对每个人进行操作;要么是维护人,对每个T恤进行操作。对这题而言,最方便的是维护人,枚举T恤对人进行操作。
我们首先将T恤按照q i qi q i q i qi q i c i ci c i c i ≤ v i ≤ 2 ∗ c i ci \le vi \le 2*ci c i ≤ v i ≤ 2 ∗ c i v i > 2 ∗ c i vi \gt 2*ci v i > 2 ∗ c i
对于第一部分,我们可以对他们直接进行暴力修改操作,每次这部分的人最少会减少一半,那么对于每个人来说,最多只会被暴力修改log v i \log{vi} log v i
对于第二部分,因为它们v i vi v i c i ci c i
代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define ls(u) tree[u].son[0] #define rs(u) tree[u].son[1] using namespace std;const int MAX = 2e5 + 10 ;struct TS { int c, q; bool operator < (const TS& rhs) const { return q == rhs.q ? (c < rhs.c) : (q > rhs.q); } } ts[MAX]; struct Node { int v, id, ans; int lazyV, lazyAns; int cnt, siz, fa, son[2 ]; } tree[MAX]; int root, idx, n, m;int tmp[MAX], tp; int ans[MAX], que[MAX], head, tail, minv = INT_MAX;void pushup (int u) tree[u].siz = tree[ls (u)].siz + tree[rs (u)].siz + tree[u].cnt; } void pushdown (int u) if (ls (u) && tree[ls (u)].id) { tree[ls (u)].v -= tree[u].lazyV; tree[ls (u)].ans += tree[u].lazyAns; tree[ls (u)].lazyV += tree[u].lazyV; tree[ls (u)].lazyAns += tree[u].lazyAns; } if (rs (u) && tree[rs (u)].id) { tree[rs (u)].v -= tree[u].lazyV; tree[rs (u)].ans += tree[u].lazyAns; tree[rs (u)].lazyV += tree[u].lazyV; tree[rs (u)].lazyAns += tree[u].lazyAns; } tree[u].lazyV = tree[u].lazyAns = 0 ; } void rotate (int x) int y = tree[x].fa; int z = tree[y].fa; int k = (rs (y) == x); pushdown (x); pushdown (y); tree[z].son[rs (z) == y] = x; tree[x].fa = z; tree[y].son[k] = tree[x].son[k ^ 1 ]; tree[tree[x].son[k ^ 1 ]].fa = y; tree[x].son[k ^ 1 ] = y; tree[y].fa = x; pushup (y); pushup (x); } void splay (int x, int goal) while (tree[x].fa != goal) { int y = tree[x].fa; int z = tree[y].fa; if (z != goal) { ((ls (y) == x) ^ (ls (z) == y)) ? rotate (x) : rotate (y); } rotate (x); } if (!goal) { root = x; } } int getPrev (int val) int u = root, p = 0 ; while (u) { pushdown (u); if (tree[u].v >= val) { u = ls (u); } else { p = u; u = rs (u); } } return p; } int getNext (int val) int u = root, p = 0 ; while (u) { pushdown (u); if (tree[u].v <= val) { u = rs (u); } else { p = u; u = ls (u); } } return p; } void insert (int val, int id, int ans, int cnt = 1 ) int u = root, fa = 0 ; while (u) { pushdown (u); fa = u; u = tree[u].son[val > tree[u].v]; } u = tp ? tmp[tp--] : ++idx; if (fa) { tree[fa].son[val > tree[fa].v] = u; } tree[u].v = val; tree[u].id = id; tree[u].ans = ans; tree[u].fa = fa; tree[u].cnt = tree[u].siz = cnt; tree[u].son[0 ] = tree[u].son[1 ] = 0 ; splay (u, 0 ); } void clean (int u) tmp[++tp] = u; tree[u].v = tree[u].id = tree[u].ans = 0 ; tree[u].lazyV = tree[u].lazyAns = 0 ; tree[u].cnt = tree[u].siz = tree[u].fa = 0 ; tree[u].son[0 ] = tree[u].son[1 ] = 0 ; } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (false ); cin.tie (nullptr ); cin >> n; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> ts[i].c >> ts[i].q; minv = min (minv, ts[i].c); } cin >> m; insert (INT_MIN, 0 , 0 ); insert (INT_MAX, 0 , 0 ); for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { int v; cin >> v; insert (v, i, 0 ); } sort (ts + 1 , ts + n + 1 ); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { int c = ts[i].c, q = ts[i].q; int L = getPrev (c), R = getNext (c + c - 1 ); splay (L, 0 ); splay (R, L); int uu = ls (R); tree[R].son[0 ] = 0 ; if (R && tree[R].v != INT_MIN && tree[R].v != INT_MAX) { tree[R].v -= c; tree[R].ans++; tree[R].lazyV += c; tree[R].lazyAns++; splay (R, 0 ); } head = -1 ; tail = 0 ; if (uu) que[++head] = uu; while (head >= tail) { int u = que[tail++]; int val = tree[u].v, id = tree[u].id, an = tree[u].ans; pushdown (u); if (ls (u)) que[++head] = ls (u); if (rs (u)) que[++head] = rs (u); clean (u); if (id && val - c >= minv) { insert (val - c, id, an + 1 ); } else if (!id) { insert (val, 0 , 0 ); } else { ans[id] = an + 1 ; } } } head = -1 ; tail = 0 ; que[++head] = root; while (head >= tail) { int u = que[tail++]; ans[tree[u].id] = tree[u].ans; pushdown (u); if (ls (u)) que[++head] = ls (u); if (rs (u)) que[++head] = rs (u); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= m; i++) { cout << ans[i] << (" \n" [i == m]); } return 0 ; }